Have you ever wondered what the largest single-celled organisms in the world are? Well, you’re in luck! We’ve compiled a list of the ten largest single-celled organisms known to man. You won’t believe how big some of these creatures are! From the mysterious ‘blob’ to the microscopic yet impressive Paramecium, there’s something for everyone in this list.
So what exactly makes a single-celled organism so unique? Well, single-celled organisms are unique because they contain only one cell, instead of the trillions of cells found in the human body. They are some of the most primitive forms of life on Earth, and yet some of them can reach sizes that would make even the largest animals envious!
Discover the fascinating world of single-celled organisms and learn all about the ten biggest single-celled organisms known to mankind. Prepare to be amazed!
Stentor
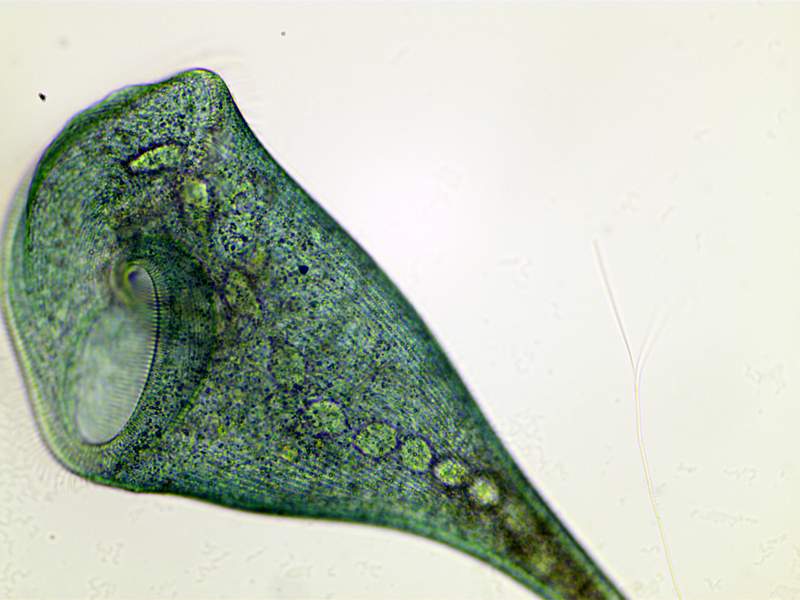
Stentor is one of the most remarkable single-celled organisms, a ciliate protozoan found in freshwater habitats. Its size ranges from 0.4 to 1.2 mm, making it visible to the naked eye. It has a trumpet-shaped body with a large and a small end, and a ring of cilia around its midsection. has a distinctive lorica, a hard outer shell that it uses for protection.
a stentor has a complex life cycle, including sexual and asexual reproduction. During asexual reproduction, it undergoes binary fission, dividing into two identical pieces. During sexual reproduction, it undergoes syngamy, in which a sperm and an egg cell fuse.
incredible organism and its ability to detect and respond to its environment make it one of the most remarkable single-celled organisms. Its size and complexity make it a fascinating and unique creature.
Spirostomum

They have a unique shape, resembling a twisted ribbon, and can be up to 2 millimeters in length. These organisms are found in both freshwater and marine environments.
Spirostomum’s most distinctive feature is its crown of cilia. The cilia beat in waves, propelling the organism forward. This unusual form of locomotion allows the organism to move quickly in its environment.
feed on bacteria and other small organisms, using their cilia to capture prey. They are also able to absorb nutrients through their cell walls. This makes them very efficient predators. is an important part of the aquatic food web, playing a vital role in the transfer of energy from one organism to another. It is also an interesting study organism, and researchers are continually learning more about its biology and ecology.
Chaos Carolinensis

Continuing from the discussion, let’s discuss another freaky single-celled organism, Chaos carolinensis. It is a species of amoeba, which is an organism that changes shape and size. This species was discovered in Lake Chaohu, located in China.
Chaos Carolinensis is in a class of its own, as it is the largest single-celled organism known to man. It can grow up to 1.5 mm in size and its shape is that of an irregular sphere. Its body is made up of a single cell that contains nuclei and various organelles.
This organism is unique in its ability to move and reproduce. It can move around its environment by extending pseudopods, or false feet. It also reproduces asexually by forming two daughter cells.
The following are some interesting facts about Chaos Carolinensis:
- It is the largest single-celled organism known to man
- It has an irregular sphere-shaped body
- It can move around by extending pseudopods
- It reproduces asexually by forming two daughter cells
With its ability to move and reproduce, Chaos carolinensis is a remarkable and freaky single-celled organism. It has the potential to teach us more about this class of organisms and their behavior in the environment.
Gromia Sphaerica
Gromia Sphaerica is an unusually large single-celled organism that can reach up to 25 cm in size. This organism was discovered in South Africa in the 1950s and is believed to be a living fossil. It is unique in its size and structure, as it is larger than any other single-celled organism known to exist.
Despite its size, Gromia Sphaerica still functions like any other single-celled organism. It has a nucleus, cytoplasm, and a cell membrane. It also has a unique structure, consisting of several concentric layers. The outermost layer is composed of a membrane made up of chitin, and the inner layers are made of calcium carbonate.
This organism is also capable of movement. It can move by using flagella and cilia, which are tiny hair-like structures. Gromia Sphaerica uses its flagella and cilia to move slowly around in the water. It is slow-moving compared to other single-celled organisms but still capable of independent movement.
Gromia Sphaerica is a fascinating organism, and its size and structure make it, unlike any other single-celled organism. Its ability to move independently and its unique structure is certainly intriguing qualities. It is an incredible example of the diversity of life on Earth and a testament to the power of evolution.
Sailor’S Eyeball
Sailor’s Eyeball is a giant single-celled organism that has been found to measure up to a whopping 10 centimeters in diameter. It is a member of the group of organisms known as ‘giganto plasmids’, which are defined as single-celled eukaryotes with a diameter of over 6 millimeters. This organism is named after the famous sailors who found them during their voyages.
Sailor’s Eyeball is a type of foraminifera, which is a group of protists that includes such organisms as amoebas and radiolarians. It is a relatively simple organism with an outer shell made of calcium carbonate plates and a single nucleus. In addition, it has an array of filaments that enable it to move and feed.
The sheer size of the Sailor’s Eyeball allows it to feed on larger organisms, such as other foraminifera and small crustaceans. It is also capable of catching particles in the water and latching onto them, which helps it to obtain nutrients. It is even able to survive in low-nutrient environments, due to its ability to accumulate and store nutrients in its cytoplasm.
All in all, Sailor’s Eyeball is an extraordinary organism that exemplifies the diverse range of life forms on our planet. It is an impressive example of the incredible adaptations single-celled organisms can possess to survive in any environment. Its sheer size and capabilities are truly remarkable.
Spiculosiphon Oceana
Moving on from sailor’s eyeball, we come to the spiculosiphon oceana, a freakishly large single-celled organism. This mysterious creature was first discovered in the depths of the Pacific Ocean in 2003. It’s a giant foram, which is a type of protist. These single-celled organisms are known for their unique shape, which looks like a spiny shell.
The spiculosiphon oceana, however, is much larger than other forams and can measure up to a few centimeters in length. It’s also unique in that it has a large, spiky shell and two long, whip-like protrusions extending from its body. These protrusions help the organism move around and catch its prey.
The spiculosiphon oceana is also known for its ability to survive in adverse conditions. It can survive in temperatures ranging from -5 to 35 degrees Celsius and in depths up to 2500 meters. This makes it one of the most resilient single-celled organisms in the ocean.
Researchers are still trying to understand the spiculosiphon oceana and how it fits into the marine ecosystem. It’s clear, however, that this unique creature is an important part of the ocean’s delicate balance. Further research may reveal more about its fascinating adaptations and behavior.
Acetabularia
Acetabularia is a genus of large single-celled organisms that have been around for millions of years. They are members of the green algae family and can reach up to 10 cm in length. Acetabularia is an incredibly fascinating species for many reasons. Here are four of them:
- It can regenerate itself when it’s damaged.
- It can survive in both saline and freshwater environments.
- It has a complex cellular structure which can be studied to learn more about its behavior.
- It is visible to the naked eye and can be studied without advanced microscopes.
Acetabularia has been studied extensively by scientists, who have learned a great deal about its behavior and its ability to adapt to its environment. This research has been instrumental in furthering our understanding of cell biology.
Acetabularia is an important organism in the study of evolution and adaptation. Its cellular structure can be studied to learn more about the evolution of cells over time. It has also been used as a model organism for studying the effects of environmental change on organisms.
Overall, Acetabularia is an incredibly interesting organism that has been studied for many years and has a lot to teach us about the evolution of cells and adaptation to the environment. Its unique cellular structure and ability to regenerate itself make it a valuable organism for research.
Syringammina Fragilissima
The cell wall of Syringammina Fragilissima is composed of silica, and its interior is filled with a jelly-like material. Its size and shape allow it to be incredibly buoyant and it can easily float in the water. It can also move in the water by using its flagella to propel itself.
Syringammina Fragilissima is incredibly fragile and can easily be damaged if mishandled. It is also susceptible to changes in its environment, such as changes in light and temperature. As a result, it is crucial for researchers to take extra care when handling this organism.
Syringammina Fragilissima is an incredible organism that has amazed researchers with its size and structure. Its unique properties make it an important organism for researchers to study and protect. It is a fascinating creature that deserves more attention and research to understand its importance fully.
Plasmodial Slime Molds
Plasmodial slime molds are a diverse group of single-celled organisms that are known for their freakishly large size. They are often found in damp, dark places such as forests and gardens, but can also be found in urban areas. They are typically yellow, orange or brown in colour, and have a slimy consistency.
The plasmodial slime molds have several unique characteristics that make them distinctive:
- They move by extending pseudopods, or false feet, from their bodies.
- They can also form fruiting bodies, which are structures that contain reproductive spores.
- They have the ability to aggregate into a large mass called a plasmodium.
Plasmodial slime molds can survive in a variety of conditions due to their ability to form plasmodia. This allows them to move around and search for food, and also allows them to spread their spores. Plasmodial slime molds usually feed on bacteria and decaying organic matter but can also feed on living organisms.
In addition to their unusual size, plasmodial slime molds can also reproduce asexually, or without the involvement of another organism. This means that they can produce offspring without mating, making them even more interesting and unique.
Plasmodial slime molds are fascinating organisms that are sure to fascinate anyone who encounters them. From their distinctive characteristics to their ability to reproduce asexually, these organisms are definitely worth further investigation.
Caulerpa Taxifolia
Caulerpa Taxifolia is an example of a freakishly large single-celled organism. It can reach sizes of up to six feet in length and is found in warm, shallow waters around the world. It has a bright green, leafy appearance and is sometimes used in aquariums as a decoration.
Caulerpa Taxifolia is an invasive species that can spread quickly and outcompete native species. It reproduces both sexually and asexually, making it difficult to control its spread. It is capable of forming dense mats over large areas of the ocean floor, blocking sunlight and preventing other species from growing.
The growth of Caulerpa Taxifolia can have serious effects on the environment. It can reduce biodiversity, cause a decrease in fish populations, and disrupt the balance of the food chain. It can also interfere with recreational activities such as swimming and fishing.
In order to prevent its spread, it’s important to take steps to prevent its introduction into new areas. This includes monitoring the movement of boats and equipment and proper disposal of aquariums and their contents. Taking these steps can help preserve the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Any Of These Single-Celled Organisms Dangerous To Humans?
The question of whether any of these single-celled organisms can be dangerous to humans is an important one. With a greater understanding of the types of single-celled organisms available, it is possible to explore the potential risks that they may pose.
The first step to understanding the potential dangers of single-celled organisms is to look at the different types of single-celled organisms. Here are some examples of these organisms:
- Bacteria
- Archaea
- Fungi
- Protozoa
Each of these organisms can have different characteristics and behaviors, making them potentially dangerous to humans. For example, some bacteria can cause serious illnesses, while some fungi can be toxic if ingested. It is important to be aware of these potential risks when dealing with single-celled organisms.
In addition to diseases and toxins, single-celled organisms can also cause physical harm. These organisms can be very small and can easily enter the human body. If a single-celled organism enters the body, it can cause irritation, infection, and even damage to organs.
Therefore, it is important to be aware of single-celled organisms’ potential dangers and take precautions when dealing with them. This includes understanding the types of single-celled organisms and their characteristics, as well as taking steps to protect yourself from their potential risks.
How Long Do Most Of These Single-Celled Organisms Live?
When it comes to single-celled organisms, one of the most pressing questions is how long they usually live. It’s a complicated subject, as there are many different kinds of single-celled organisms, and their lifespans can vary drastically. Fortunately, a few general guidelines can be used to get an idea of how long most of these organisms live.
The first thing to consider is the type of single-celled organism. For example, some types of single-celled organisms, such as protozoa, can live for several years. On the other hand, some bacteria can only live for a few days or weeks. In addition, the single-celled organism’s environment can also affect its lifespan. For instance, a single-celled organism living in an environment with ample food and favorable temperatures can typically live longer than one living in an environment with poor nutrition and extreme temperatures.
The second factor to consider is the size of the single-celled organism. Generally speaking, larger single-celled organisms tend to live longer than smaller ones. This is because larger organisms have more energy and resources available to them, and can thus survive for longer periods of time.
Finally, the age of the single-celled organism can also play a role in its lifespan. For example, an older organism may have accumulated damage over time, making it more susceptible to death than a younger one. Similarly, younger organisms may be more resilient, allowing them to live longer.
In summary, the lifespan of a single-celled organism can vary greatly depending on the type, environment, size, and age of the organism. With this information in mind, it’s possible to get a better understanding of how long most single-celled organisms live.
Does The Size Of These Single-Celled Organisms Vary?
When it comes to single-celled organisms, one of the questions that often arises is whether their size varies. In order to answer this question, it’s important to first understand the general characteristics of these organisms.
Single-celled organisms are generally microscopic in size and can survive in a variety of environments. They are able to carry out metabolic processes without having a complex internal structure. As a result of these traits, single-celled organisms have become one of the most common forms of life on Earth.
Despite their small size, there are some single-celled organisms that are surprisingly large. In fact, these creatures can range from a few micrometers to hundreds of micrometers in size. Here are some characteristics of these freakishly large single-celled organisms:
- They tend to be more complex than their smaller counterparts.
- They are often multinucleated and can contain hundreds of nuclei.
- They are able to perform more advanced metabolic processes.
- They can form colonies with other single-celled organisms.
The size of single-celled organisms can vary greatly depending on the species. While many are microscopic, some are larger than most people would expect. This is especially true for certain species that have evolved to become larger over time. Ultimately, it’s clear that size is not a defining characteristic of single-celled organisms.
Are These Single-Celled Organisms Found In All Types Of Environments?
Are these single-celled organisms found in all types of environments? This is a pertinent question to consider when examining the wide variety of single-celled organisms that exist in the world. It is important to note that single-celled organisms exist in both terrestrial and aquatic environments.
It is also worth noting that single-celled organisms are found in a variety of shapes and sizes. Some of these organisms are very small, while others are freakishly large. This can be seen in the 10 freakishly large single-celled organisms which are often discussed in the scientific community.
When looking at the environments in which these single-celled organisms are found, it is clear that they are not limited to one specific type of environment. For example, some of these organisms are found in freshwater environments, while others are found in saltwater environments. Additionally, some of these organisms are also found in soil, air, and even in the human body.
It is clear that single-celled organisms can be found in a variety of environments and that they come in different shapes and sizes. Understanding the diversity of these organisms can help us better understand the complexity of the world in which we live.
Are Any Of These Single-Celled Organisms Beneficial To Humans?
Are any of these single-celled organisms beneficial to humans? This is an important question to ask, particularly given the vast array of organisms that live on our planet. While some of these microscopic life forms may appear to be too small to have any significance in our lives, there are surprisingly many that have contributed significantly to human health. Here are a few of the ways these single-celled organisms have been beneficial to us:
- Certain yeasts have been used to produce bread, beer, and wine.
- Algae are used in some foods as thickeners and stabilizers.
- Miniature worms known as nematodes can be used as biological pest control.
- Bacteria are used to produce antibiotics and other medicines.
- Fungi can be used to make food and fuel.
The use of these single-celled organisms in food and medicine has been a major boon to humans throughout history. For example, the use of yeasts in fermentation has enabled us to produce a variety of alcoholic beverages, as well as bread and other baked goods. In addition, the use of algae, nematodes, bacteria, and fungi in food production has helped us to feed more people with less effort.
In terms of medicine, single-celled organisms have been used to produce a variety of antibiotics and other drugs that have saved countless lives. For instance, the antibiotic penicillin was discovered in 1928 when a Scottish scientist noticed that some bacteria were unable to grow near a certain strain of mold. This discovery led to the development of a number of other antibiotics, which are still used today to treat a wide range of conditions.
Single-celled organisms have also been used in the production of renewable energy sources. For example, some species of algae can be used to produce biofuel, while others can be used to create methane gas. This has the potential to drastically reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and help to reduce our impact on the environment.
Clearly, single-celled organisms have been a major asset to humanity over the centuries. From providing us with food to helping us fight disease and even creating renewable energy sources, these tiny organisms have played a crucial role in our lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s clear that single-celled organisms come in a variety of sizes, and some of them can be quite large. Although some of these organisms may not be dangerous to us, it’s still important to take precautions with all types of single-celled organisms.
It’s also interesting to note that these single-celled organisms can live for quite a long time and can be found in a variety of environments. This means they can be found almost anywhere and adapt to their surroundings.
Overall, some of these organisms can be beneficial to us, such as algae, which can be used to create biofuels. It’s also important to remember that these single-celled organisms can have negative effects as well, such as causing disease. Therefore, it’s important to be mindful of single-celled organisms and their potential implications.
